|
The publication of the three dimensional structure of DNA in 1953 was a groundbreaking advance in biology. Understandingt the structure of DNA allowed scientists to determine the relationship between DNA, RNA, and proteins commonly referred to as the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology. By understanding the components of DNA and how they are put together allowed us to understand how the DNA molecule can store genetic information and how cells are able to retrieve and use this information to build molecules that determine traits such as hair color or blood type.
In the video you will learn how to fold an origami model of DNA. The handout for this activity is available at the bottom of this post to be downloaded if you want to try folding your own DNA model! The model does a really nice job of illustrating some key ideas that are critical to developing a full understanding of DNA.
This next video shows a summary of a Flash Activity from the Learn Genetics website that allowed users to build a virtual model of DNA. The video also summarizes key ideas important to understanding DNA structure.
2 Comments
The model below show a 3D representation of sucrose (table sugar).
In this simulation, students will review the three major types of intermolecular forces—London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole interactions, and hydrogen bonding—through short video clips and accompanying text. They will then answer quiz questions using the relative strengths of these forces to compare different substances given their name, formula, and Lewis structure, and put them in order based on the strength of their intermolecular forces, their boiling point, or their vapor pressure.
This activity was made available by the American Association of Chemistry teachers and can also be found at: teachchemistry.org
In my last post, I shared Mark Rober's TEDx presentation "The Super Mario Effect - Tricking Your Brain into Learning More" when he discussed the idea of using gamification to increase how much you can learn. In the talk, Rober discusses how two groups were given the task of writing code to direct a car through a video game maze. The experiment found that participants who were not assessed penalties stayed with the challenge more than two times longer than participants who were assessed a penalty for submitting code that had an error. The group that was not penalized had a success rate that was 16% higher (68% vs. 52%) than the group that was penalized.
Rober continues his talk be sharing his personal experiences playing video games in his childhood. He makes a case that a gamification model of learning which allows learners multiple attempts at a task with no penalties can lead to more significant learning gains than would be possible in a more traditional approach which penalizes learners for making mistakes along the way. I teach an integrated science class which incorporates biology, chemistry, physics and Earth and space sciences into a single course. Mark's video has inspired me to transition this class into a gamified delivery structure. So what does gamification look like in the science classroom? One example I've created uses laboratory video of the combustion of magnesium (Mg) and uses H5P to add interactive questions to the video that allow the viewer to answer the questions, receive immediate feedback and attempt the question until they are able to answer it correctly. The goal I have for this school year is to have students engage in activities where they are able to receive timely feedback from videos like the example above, web based practice quizzes that give immediate feedback, peer feedback and direct teacher feedback as well. Students will be able to continue to make attempts at these tasks until they master skills like performing conversion calculations, balancing chemical equations, interpreting DNA sequence data and more... I chose a science fiction theme for the gamification model which is based in humanity's near future. I chose this theme partly because of my own interest in hard science fiction and also because of my involvement with the Astronomy club at the school where I teach. Our club has been able to recruit guest speakers from NASA, JPL and other aerospace industry professionals. The storylines in class will begin in the year 2050 and will be based on current developments in space exploration like the Mars 2020 mission, the Artemis program, APL's Dragonfly mission to Titan and ESA and Chinese missions to Mars. My ideas for the storylines are very much inspired by my love of "The Expanse" telivision and book series. The storylines will attempt to tell the story of how human expansion into the solar system takes place. I have created a trailer for the class which I hope will help to inspire my students. The storylines during the fall semester will be heavily focused on biology and chemistry. One storyline which will be incorporated into first quarter will involve students planning a drone robotic balloon mission to Venus to search for evidence that life might exist in the upper atmosphere. Lessons will focus on the molecules of life (DNA and other macromolecules), life processes such as cell division, plus chemistry topics including gas laws and stoichiometry. The Venus mission storyline would draw inspiration from the proposed NASA missions called HAVOC (High Altitude Venus Operational Concept) that would use lighter than air craft to explore the upper atmosphere of Venus. In my next post I'll share my plans for utilizing elements of the ungrading instructional philosophy and connect it to Mark Rober's coding challenge experiment.
I have a confession to make, I love Mark Rober! I mean, what's not to like about the guy? He's smart, funny and seems to have the YouTube algorithm in his back pocket. My kids love him too! Their favorite videos are the backyard squirrel mazes. We are currently building our own squirrel obstacle course in our yard and my son really wants to sign up for Mark's online engineering course. I've promised him we will sign up next summer. Hold us a spot Mark, looks like the class fills up fast!
Mark's video that inspired me to make some major changes to my teaching was a TEDx called "The Super Mario Effect - Tricking Your Brain into Learning More" in which Mark described an experiment he ran on his YouTube channel. 50,000 viewers who participated in a coding challenge were randomly placed into two groups. Users started with 200 points and were randomly placed into two groups that would receive different types of feedback after attempting to run the code they had written to move a car through a virtual maze.
In one experimental group, a user who attempted to run code that did not work would see the message "That didn't work. Please try again." These users were not penalized points. Users in the other group would see the following message if their code did not work. "That didn't work. You lost 5 points. You now have 195 points. Please try again." It was really the data from Mark's experiment that got me thinking. The users who were penalized points had a 52% success rate compared to a 68% success rate for users who were not penalized. Also very interesting was the fact that participants who received penalties averaged 5 attempts before writing successful code, while the group that was not penalized on average made 12 attempts before succeeding. The logical conclusion from the data was that participants who were not penalized for making a mistake were much more likely to keep trying until they were successful. I'm not a bad science teacher; I like to think that I usually do a pretty good job. But along the way, I could have done a better job for some of my students. Mark's video showed that his viewers were more likely to keep trying until they succeeded if they were not penalized for making mistakes. If want to do everything in my power to encourage my students to keep trying and to help them be successful, why wouldn't I make my classroom pratices more like the experiment when participants received positive encouragement without penalties? This realization has inspired me to change how I teach and grade my students. I've decided to use gamification and ungrading to make my students' experiences be more like unpenalized group in Mark's experiment. In future posts I'll share my plans for how I will change my teaching style. My next post will share the class trailer video and storyline ideas for the universe our gamified science class will exist in.
Where do nature's building blocks, called the elements, come from? They're the hidden ingredients of everything in our world, from the carbon in our bodies to the metals in our smartphones. To unlock their secrets, David Pogue, technology columnist and lively host of NOVA's popular "Making Stuff" series, spins viewers through the world of weird, extreme chemistry.
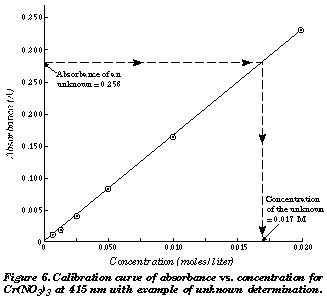
Aired: 04/03/12 Rating: TV-PG video source: https://www.pbs.org/video/nova-hunting-the-elements/ Answer:You will use Beer's law. A = εmCl Explanation: The basic idea here is to use a graph plotting Absorbance vs. Concentration of known solutions. Once you have that you can compare the absorbance value of an unknown sample to figure out its concentration. http://intro.chem.okstate.edu/ChemSource/Instrument/inst4.htm You will be applying Beer's law to calculate the concentration. The equation for Beer's law is: A = εmCl (A=absorbance, εm = molar extinction coefficient, C = concentration, l=path length of 1 cm) You should have a data set which was used to create a standard curve. The graph should plot concentration (independent variable) on the x-axis and absorption (dependent variable) on the y axis. You'll need to add a line of best fit to the data points and determine the equation for the line. The equation should be in y=mx + b form. y = absorbance (A) Note: no unit for absorbance x = concentration (C) Note: unit is M or mol/L m = (εm) = slope or the molar extinction coefficient in beers law which has units of M−1cm−1 So A = εmC +b If you solve for C you should get C = (A-b)/εm So if you substract your y-intercept from the absorbance and divide by the slope, you are finding the concentration of your sample. Here is video of a lab applying this concept.
This simulation from PhET is a great way to review parts of a wave with students. They can explore the relationships of frequency, wavelength and speed of waves. This simulation can be used in place of the classic slinky lab commonly used to teach these concepts.
This simulation allows you to explore the relationship of carbon dioxide, water vapor and atmospheric temperatures. Discover how feedback loops connect carbon dioxide, water vapor levels and temperature. The simulation also allows you to learn about albedo and changes in glacial and sea ice. Another cool feature is the ability to manipulate the amount of CO2 being emitted by human activities.
NGSS Connections: HS-ESS2-2 and HS-ESS2-4 |
Noel PaullerThank for visiting my blog where I post thoughts from the random corner of the universe which is my brain. Archives
October 2022
|


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
